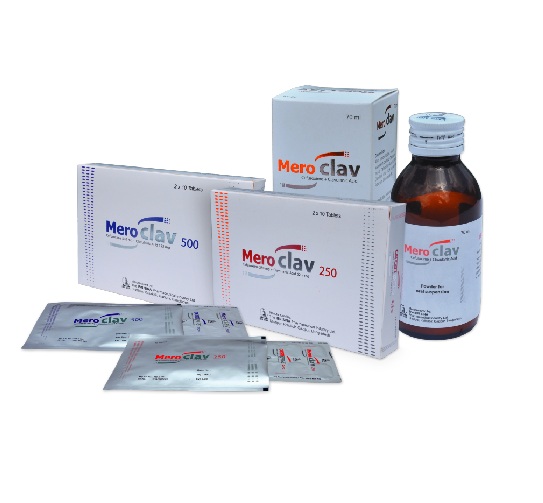
MEROCLAV
CEFUROXIME USP & CLAVULANIC ACID BP
| NAME | STRENGTH | PACK SIZE | DOSAGE FORM |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEROCLAV 250 MG & 62.5 MG | 250 MG & 62.5 MG | 20 S | TABLET |
| MEROCLAV 500 MG & 125 MG | 500 MG & 125 MG | 20 S | TABLET |
| MEROCLAV (125 MG+ 31.25MG)/5 ML | (125 MG+ 31.25MG)/5 ML | 70 ML | POS |
Meroclav 250: Each film coated tablet contains Cefuroxime 250 mg as Cefuroxime Axetil USP and Clavulanic Acid 62.5 mg as diluted Potassium Clavulanate BP.
Meroclav 500: Each film coated tablet contains Cefuroxime 500 mg as Cefuroxime Axetil USP and Clavulanic Acid 125 mg as diluted Potassium Clavulanate BP.
Meroclav 70 ml powder for suspension: After reconstitution, each 5 ml suspension contains Cefuroxime 125 mg as Cefuroxime Axetil USP and Clavulanic Acid 31.25 mg as diluted Potassium Clavulanate BP.
Meroclav tablet and powder for suspension should be kept in a cool (15°–25° C temperature) and dry place and protected from light.
Meroclav 250 : Each box contains 2x10 tablets in Alu-Alu blister pack.
Meroclav 500 : Each box contains 2x10 tablets in Alu-Alu blister pack.
Meroclav Suspension: Each bottle contains dry powder for 70 ml suspension with a measuring spoon.
